Variables
A variable is a place to store a value. The value can be anything: a text, a numeric, a data frame, etc. The value can later be used in R by simply typing the name of the variable.
A variable is created when you assign a value to it. There are three symbols used to assign a value to a variable:
<-: The name of the variable is on the left of the symbol and the value is on the right.->:The name of the variable is on the right of the symbol and the value is on the left.=: The name of the variable is on the left of the symbol and the value is on the right.
Although there are many ways to assign a value to a variable,
<-is the most commonly used symbol to do so!
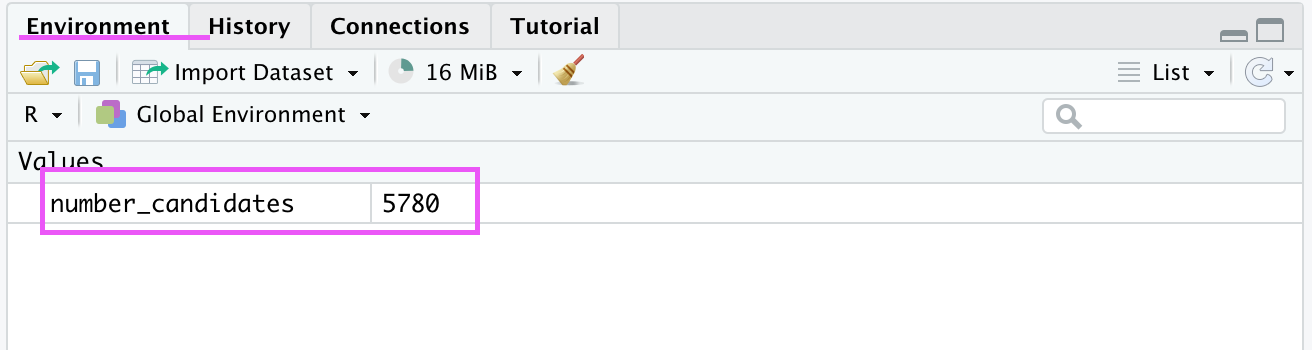
You have a study that has 5780 candidates. You would like to store that number in a variable:
number_candidates <- 5780
In this line of code, we assigned the value 5780 to the variable number_candidates. R will store the variable and its value assigned in the current workspace. You can view all variables in the workspace in RStudio in the ‘Environment’ tab in the top right corner.
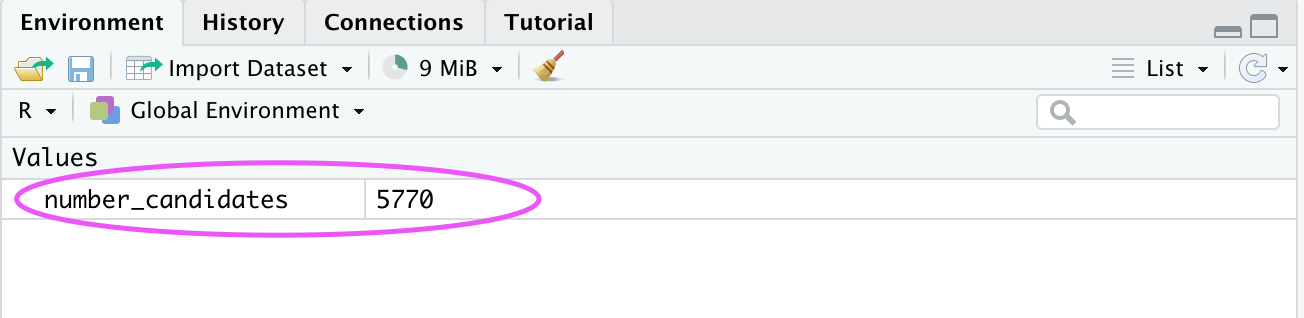
To change the value of a variable, you need to reassign the new value using <-. The new value will replace the previous value
Some candidates decided to not participate in the study, you have now around 5770 candidates. Assign a new value to the variable:
number_candidates <- 5770
This change is also reflected in the workspace in RStudio:
Rules for Naming Variables
- A variable name can contain letters, numbers, dots and underscores.
- A variable cannot start with a number, dot or an underscore.
- R is case-sensitive (
NUMBER,Numberandnumberare all different variables.) - The variable should not have the same name as functions.
Printing Variables
If you would like to see the contents of a variable, you can simply type out the name of the variable in the console.
You can also use the print() function to print the value of variables.
colour_favourite <- "blue"
#auto-print the value of the name variable
colour_favourite
Output: [1] "blue"
#using the print() function:
print(colour_favourite)
Output: [1] "blue"
You can use the cat() or the paste() function to combine variables.
#using the cat() function:
cat("My favourite colour is", colour_favourite)
Output: My favourite colour is blue
#using the paste() funtion:
paste("My favourite colour is", colour_favourite)
Output: [1] "My favourite colour is blue"
It is also possible to assign one value to multiple variables at once:
breakfast_1 <- lunch_1 <- dinner_1 <- "Tuna sandwich"
paste(breakfast_1, lunch_1, dinner_1)
Output: [1] "Tuna sandwich Tuna sandwich Tuna sandwich"